Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept, it is an actual part of our daily lives. From the algorithms that create our social media feeds to the automobiles navigating our streets, AI has crept itself into nearly every aspect of society. While it offers numerous opportunities for innovation and efficiency, it also raises significant ethical, social and economic concerns.
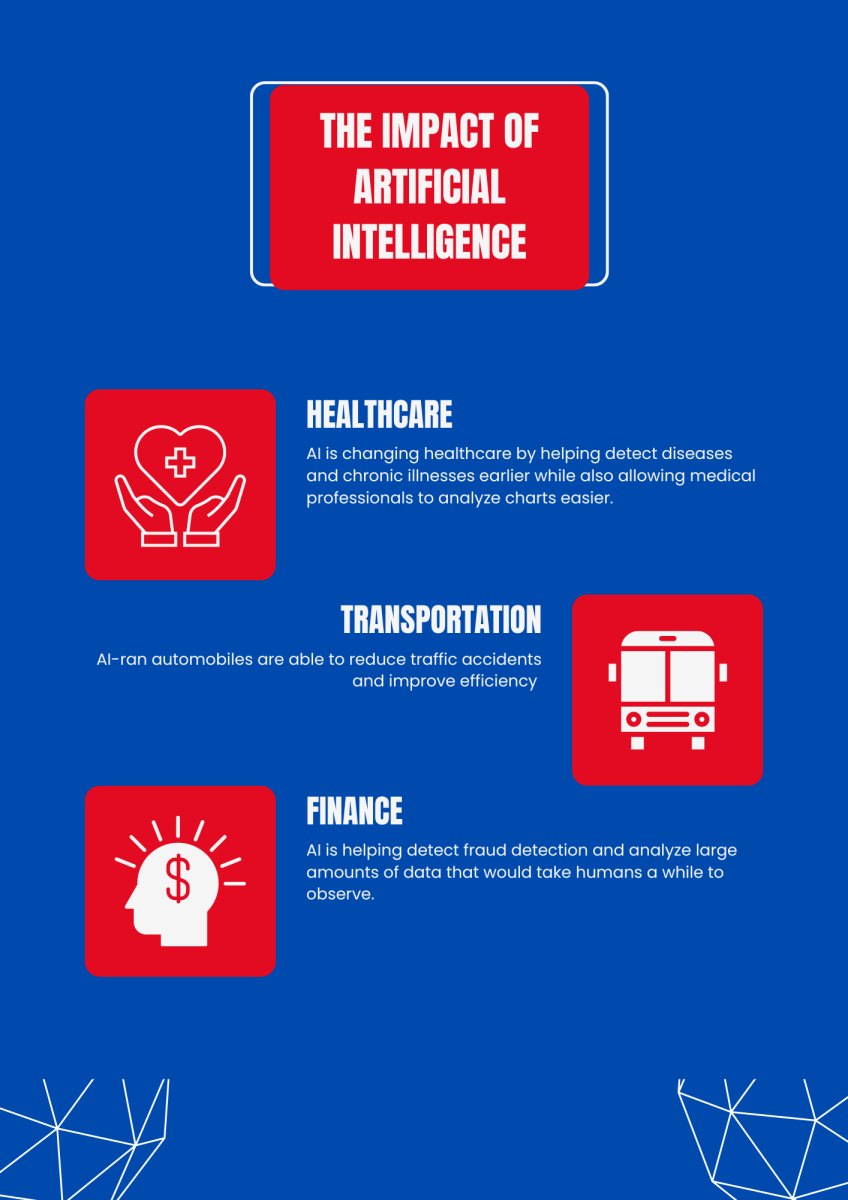
There are many benefits AI could provide for us. In healthcare, AI-driven tools are revolutionizing diagnostics and treatment plans, helping lead to earlier detection of diseases and personalized care that once seemed impossible. For instance, The National Library of Medicine identified clinicians’ views on AI and how it can offer in depth analysis on a patients records. AI algorithms can now read medical images with a level of accuracy that competes with or even surpasses human experts, leading to faster and more precise diagnoses. Even in finance, AI is creating trading strategies and enhancing fraud detection to help protect consumers and businesses.
Moreover, AI is pushing innovation in industries such as manufacturing, where robotics and automation are increasing productivity and reducing costs. AI-ran automobiles promise to transform transportation by reducing traffic accidents and improving efficiency. In the area of entertainment, AI-powered recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix and Spotify have transformed how we can discover content, offering personalized experiences for everyone.
However, the rapid proliferation of AI also comes with challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the potential for job displacement. As AI and automation continue to advance, millions of jobs—particularly those involving routine, repetitive tasks—are at risk of being eliminated. A study by the Brookings Institution found that approximately 25% of U.S. jobs are at high risk of being replaced with AI, with lower-wage workers being the most vulnerable. This could affect income inequality and create economic instability if measures are not taken in the future.
Another major concern is the ethical implications of AI. The algorithms that power AI systems are often confusing for most, making it difficult to understand how decisions are made. This lack of transparency can lead to biased outcomes, particularly when AI is used in sensitive areas such as hiring, lending, or law enforcement. For example, information collected from the ACLU have shown that facial recognition technology, a form of AI, can exhibit racial and gender biases, leading to false identifications and unjust consequences.
Furthermore, the concentration of AI development and deployment in the hands of a few large tech companies raises concerns about data privacy and monopolistic practices. These companies have large amounts of data at their disposal, enabling them to tweak their AI systems continuously. However, this also means they hold significant power over how information is processed and put out, potentially influencing public opinion.
The prevalence of AI in today’s world presents both extraordinary opportunities and significant challenges. As it becomes clearer that there is a promise of innovation in the future, it also raises more concerns and questions. The unknown impact of AI should serve as reminders to use it with discretion.